Introduction to Begonia Maculata
Begonias are some of the most widely loved plants in the horticultural world, prized for their brilliant colors, unique foliage, and easy care. One specific cultivar that has captured the hearts of plant enthusiasts is the Begonia Maculata. With its eye-catching foliage and adaptability, this plant stands out among the vast begonia species. This article delves deep into the world of Begonia Maculata, its origin, characteristics, care tips, and frequently asked questions. If you’re a plant enthusiast or are looking for a new addition to your garden or home, this guide will equip you with everything you need to know about Begonia Maculata.
Table of Contents
- The Origins of Begonia Maculata

Begonias, native to tropical and subtropical regions, boast over 2,000 different species. The Begonia Maculata is a relatively recent hybrid named after Maculata, a picturesque coastal town in Victoria, Australia. This cultivar was specifically bred for its striking foliage, ease of care, and ability to thrive indoors as a houseplant or outdoors in gardens with temperate climates.
The name “Begonia” originates from Michel Bégon, a French plant enthusiast and a governor of French colonial territories, who promoted the study of plants in the 17th century. The genus Begonia became known in his honor after his death. Begonia Maculata carries on this legacy, as it has become a popular choice in ornamental gardening across the world.
- Characteristics of Begonia Maculata
2.1 Foliage
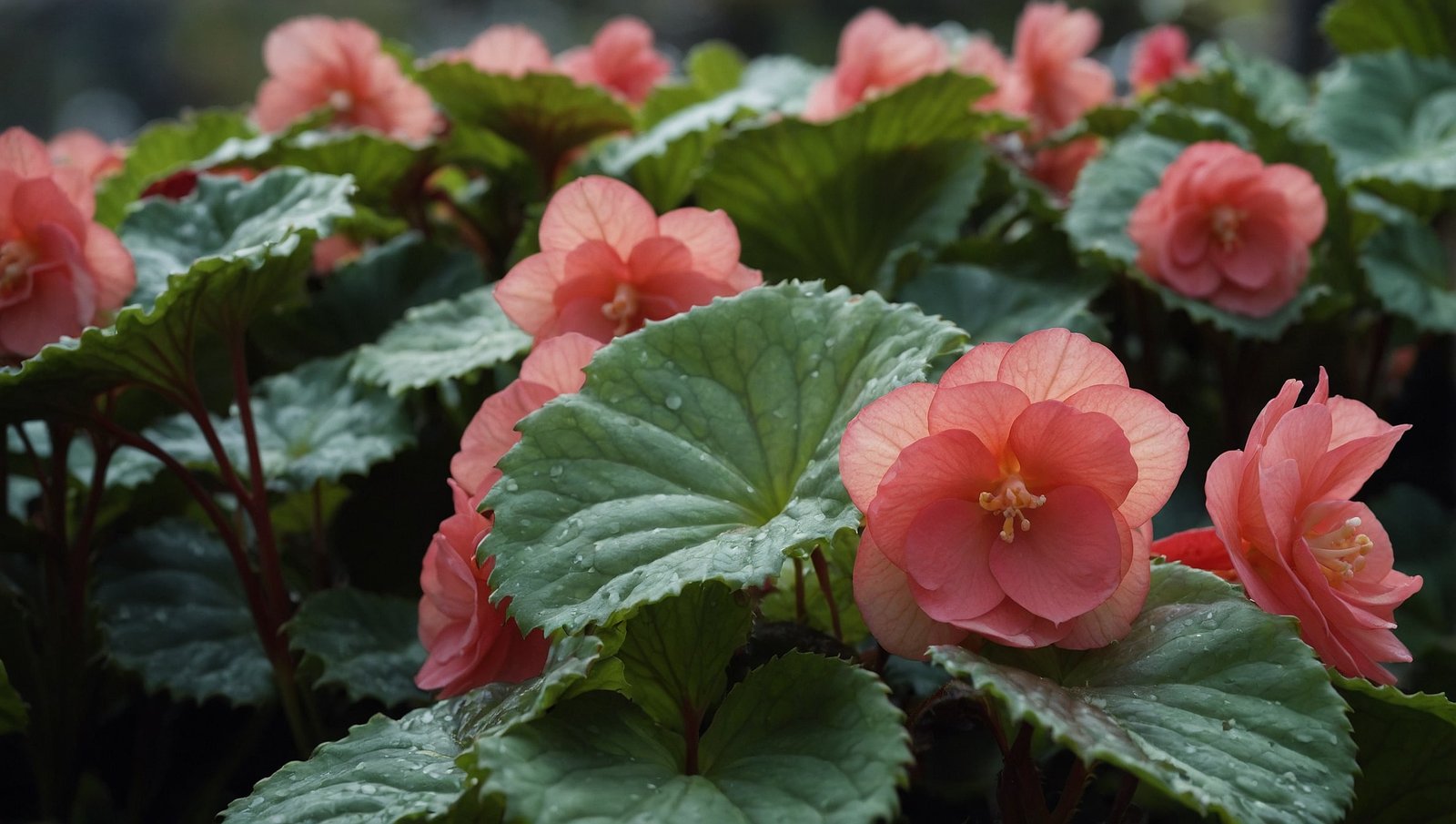
Begonia Maculata is especially famous for its intricate foliage. The leaves are typically asymmetrical, which is a trademark feature of most begonias. The leaves have a deep green base color, often splashed with shades of silver, white, or red. This marbling effect gives the plant a dramatic and ornamental appeal. Each leaf is deeply textured, adding dimension and complexity to its appearance.
The underside of the leaves can often be a contrasting dark red or purple, providing even more visual interest. The combination of bright, variegated tops and richly colored undersides makes Begonia Maculata a standout plant in any collection.
2.2 Size and Growth Habit
Begonia Maculata is considered a medium-sized begonia, typically growing between 12-18 inches (30-45 cm) tall. It has a compact and bushy growth habit, which makes it perfect for container gardening or as an indoor houseplant. The plant grows from thick, fleshy rhizomes, which store water, helping the plant tolerate occasional dry conditions.
Its growth habit is typically mounded, with leaves radiating outwards from the center of the plant. While begonias are generally known for their flowers, Begonia Maculata is grown primarily for its striking foliage. That said, it does occasionally produce delicate pink or white flowers, though these are typically considered less significant than the plant’s leaves.
2.3 Flowering
Though flowers are secondary to its stunning foliage, Begonia Maculata can bloom under the right conditions. It produces clusters of small, white to pale pink flowers that emerge on slender stalks. These blooms usually appear during late spring to early summer, but in some cases, the plant may flower sporadically throughout the year. While not the primary reason for growing this begonia, the flowers do add a delicate beauty that complements the plant’s intricate leaves.
- Care Tips for Begonia Maculata

Caring for Begonia Maculata is relatively straightforward, making it an ideal plant for both novice and experienced gardeners alike. However, like all plants, it thrives best under specific conditions.
3.1 Light Requirements
Begonia Maculata prefers bright, indirect light. Direct sunlight can cause leaf burn, leading to scorched or bleached leaves. When grown indoors, place the plant near an east or north-facing window where it will receive ample light without the harshness of the midday sun. If grown outdoors, ensure it’s placed in a location with dappled sunlight or partial shade.
In low-light conditions, the plant may become leggy, with elongated stems and fewer leaves. To prevent this, try to provide as much bright, indirect light as possible.
3.2 Watering
One of the key elements of caring for Begonia Maculata is ensuring proper watering. The plant prefers consistently moist, but not waterlogged, soil. Water when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Overwatering can lead to root rot, so ensure the plant is in a well-draining pot with sufficient drainage holes.
In contrast, underwatering can cause the plant’s leaves to dry out and become crispy at the edges. The key is finding a balance between keeping the soil evenly moist and allowing it to dry out slightly between waterings.
3.3 Humidity and Temperature
Begonia Maculata thrives in environments with moderate to high humidity. If grown indoors, consider placing a humidifier nearby or placing the plant on a tray filled with pebbles and water to increase humidity. In outdoor settings, it will thrive in humid climates or areas with morning dew.
The plant prefers temperatures between 60-75°F (15-24°C). It is sensitive to cold drafts and sudden temperature changes, which can cause the leaves to drop. It is essential to avoid placing the plant near air conditioning vents, heaters, or drafty windows.
3.4 Soil
Begonia Maculata requires a well-draining soil mix. A commercial potting mix designed for houseplants or specifically for begonias works well. To enhance drainage, you can amend the soil with perlite or coarse sand. Avoid using heavy or clay soils, as they retain too much water and increase the risk of root rot.
3.5 Fertilizing
During the growing season, typically spring through early autumn, Begonia Maculata benefits from regular feeding. Use a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength every 2-4 weeks. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to salt buildup in the soil, which may harm the plant. During the winter months, when growth slows, reduce or stop fertilizing altogether.
3.6 Pruning
Pruning helps maintain the plant’s bushy and compact form. Regularly remove any dead or yellowing leaves to encourage healthy growth. If the plant becomes leggy, you can prune back the stems to encourage branching. This will result in a fuller, more attractive plant.
- Propagation of Begonia Maculata

Propagation is a rewarding way to increase your collection of Begonia Maculata. There are two main methods of propagating this plant: by stem cuttings or leaf cuttings.
4.1 Propagating by Stem Cuttings
Choose a healthy stem with at least 2-3 leaves.
Using clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears, cut the stem just below a node.
Remove the lower leaves, leaving only 1-2 at the top.
Place the cutting in a container of water or directly into a well-draining potting mix.
If using water, change the water every few days to prevent stagnation.
In a few weeks, roots should begin to develop. Once roots are a few inches long, you can transplant the cutting into soil.
4.2 Propagating by Leaf Cuttings
- Choose a healthy, mature leaf.
- Cut the leaf into sections, ensuring each section has a portion of the main vein.
- Place the leaf sections vein-side down on moist potting mix.
- Cover the container with a plastic bag or dome to create a mini greenhouse effect.
- Keep the soil moist, and in a few weeks, small plantlets should emerge from the veins.
- Common Pests and Problems
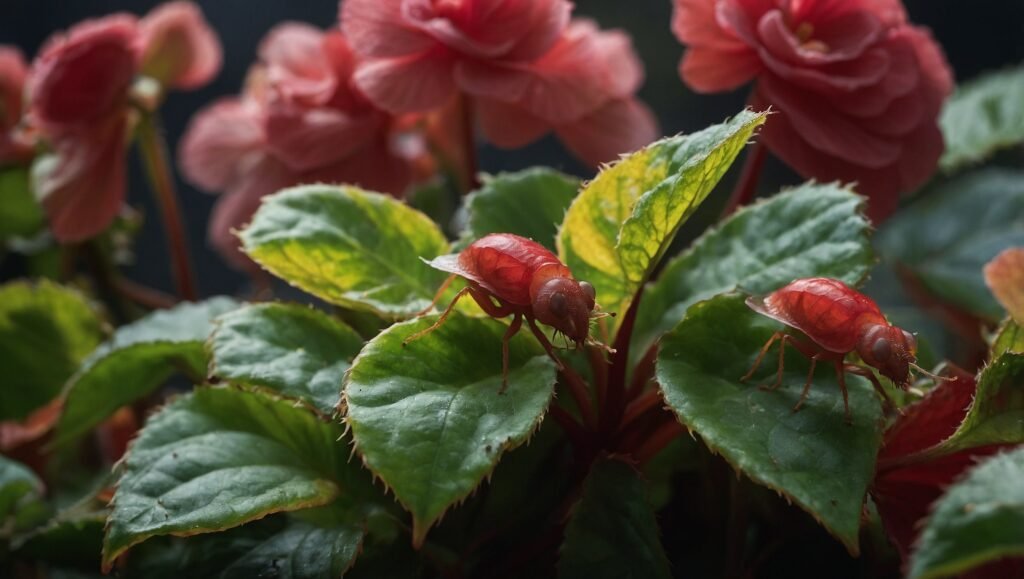

Despite being relatively low-maintenance, Begonia Maculata is not immune to pests and diseases.
5.1 Pests
Some of the most common pests that affect Begonia Maculata include:
- Aphids: These small, sap-sucking insects can cluster on new growth, leading to distorted leaves.
- Spider Mites: These tiny pests often leave a web-like residue on the plant and can cause yellowing or stippling of the leaves.
- Mealybugs: These pests appear as white, cottony masses on the stems and undersides of leaves.
To control these pests, you can use insecticidal soap, neem oil, or wipe the plant with a cloth dipped in diluted rubbing alcohol.
5.2 Diseases
Powdery Mildew: This fungal disease appears as a white powdery substance on the leaves. It thrives in humid conditions and poor air circulation. To prevent it, ensure your plant has good airflow and avoid overhead watering.
Root Rot: Overwatering or poorly draining soil can lead to root rot, which causes the roots to become mushy and the plant to wilt. If you suspect root rot, remove the plant from its pot, trim away the affected roots, and repot in fresh soil.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How often should I water my Begonia Maculata?
Water your Begonia Maculata when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Typically, this means watering once every 5-7 days, but this can vary depending on the humidity and temperature of your environment. - Can Begonia Maculata be grown outdoors?
Yes, Begonia Maculata can be grown outdoors in temperate climates. However, it prefers partial shade and protection from strong winds and harsh sunlight. In areas with cold winters, it’s best to bring the plant indoors. - What type of soil is best for Begonia Maculata?
Begonia Maculata thrives in a well-draining soil mix. A potting mix designed for houseplants or begonias works well. You can also add perlite or coarse sand to improve drainage. - Why are the leaves of my Begonia Maculata turning yellow?
Yellow leaves can be a sign of overwatering, poor drainage, or a lack of humidity. Check the soil moisture and ensure the plant is in a well-draining pot. Additionally, misting the plant or increasing the humidity in the room may help. - Is Begonia Maculata safe for pets?
Begonias, including Begonia Maculata, are toxic to pets if ingested. The plant contains soluble calcium oxalates, which can cause irritation to the mouth, vomiting, and difficulty swallowing. It’s best to keep this plant out of reach of curious pets. - How can I increase humidity for my Begonia Maculata indoors?
To increase humidity, you can place a humidifier near the plant, use a pebble tray with water, or group it with other humidity-loving plants. Avoid placing the plant near heaters or air conditioning vents, which can dry out the air. - Can I propagate Begonia Maculata in water?
Yes, Begonia Maculata can be propagated in water. Simply take a stem cutting, remove the lower leaves, and place it in a container of water. Change the water every few days, and within a few weeks, roots should begin to form. - How often should I fertilize my Begonia Maculata?
During the growing season (spring through early autumn), fertilize your Begonia Maculata every 2-4 weeks with a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength. Reduce or stop fertilizing during the winter months when growth slows. - What should I do if my Begonia Maculata is getting leggy?
If your plant becomes leggy, this usually means it’s not receiving enough light. Move it to a brighter location with indirect sunlight. You can also prune back the stems to encourage bushier growth.
Conclusion
Begonia Maculata is an exceptional plant that brings both beauty and elegance to any indoor or outdoor space. Its striking foliage, easy-care requirements, and adaptability make it a favorite among plant enthusiasts. By following the care tips outlined in this guide, you can ensure your Begonia Maculata thrives for years to come. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, this plant is sure to become a cherished part of your collection.
Here’s the wiki for more information.







Leave a Reply